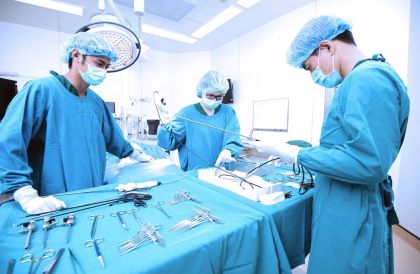
Surgical technologists, also called operating room technicians, assist in surgical operations. They prepare operating rooms, arrange equipment, and help doctors during surgeries. Before an operation, surgical technologists prepare the operating room by setting up surgical instruments and equipment. They also prepare patients for surgery by washing and disinfecting incision sites, and positioning the patients on the operating table. Surgical technologists prepare sterile solutions and medications used in surgery and check that all surgical equipment is working properly. Lastly, they help the surgical team put on sterile gowns and gloves.
Surgical technologists wear scrubs (special sterile clothing) while they are in the operating room. Their work may be physically demanding, requiring them to be on their feet for long periods. Surgical technologists also may need to help move patients or lift heavy trays of medical supplies. At times, they may be exposed to communicable diseases and unpleasant sights, odors, and materials.
During an operation, surgical technologists pass instruments and supplies to surgeons and first assistants. They also hold retractors, hold internal organs in place during the procedure, or set up robotic surgical equipment. Technologists also may handle specimens taken for laboratory analysis. Once the operation is complete, surgical technologists may apply bandages and other dressings to the incision site. They may also help transfer patients to recovery rooms and restock operating rooms after a procedure. Surgical first assistants have a hands-on role, directly assisting surgeons during a procedure. For instance, they may help to suction the incision site or suture a wound.
Surgical technology programs are offered by community colleges, technical schools, and some universities. The duration of these programs varies, with certificate and diploma programs usually taking about one year to complete, while associate degree programs typically require two years of study. The curriculum includes coursework in anatomy, physiology, microbiology, pharmacology, medical terminology, and surgical procedures.
In addition to classroom instruction, surgical technician programs require students to complete clinical training in a hospital or surgical center. This hands-on experience is crucial for developing the practical skills needed to assist surgeons and other medical professionals during surgical procedures. During their clinical training, students learn to sterilize equipment, prepare operating rooms, handle surgical instruments, and assist with patient care before, during, and after surgery.
After completing an accredited surgical technology program, graduates are eligible to sit for certification exams to become a Certified Surgical Technologist (CST) or Tech in Surgery – Certified (TS-C). The CST exam is administered by the National Board of Surgical Technology and Surgical Assisting (NBSTSA), while the TS-C exam is offered by the National Center for Competency Testing (NCCT).
Certification through the National Board of Surgical Technology and Surgical Assisting allows the use of the title Certified Surgical Technologist (CST). Certification typically requires completing an accredited formal education program or military training program and passing the examination. To maintain certification, surgical technologists must engage in continuing education and renew their certification every few years, ensuring they stay current with advancements in surgical technology and best practices in patient care.
Most surgical technologists work full time. Surgical technologists employed in hospitals may work or be on call during nights, weekends, and holidays. They may also be required to work shifts lasting longer than 8 hours. Employment of surgical technologists is projected to grow 12 percent to 2026, faster than the average for all occupations. Advances in medical technology have made surgery safer, and more operations are being done to treat a variety of illnesses and injuries. For example, an individual may decide to have a knee replacement operation in order to maintain an active lifestyle or to have cataracts removed to improve vision.
Rhinoplasty (RIE-no-plas-tee) is surgery that changes the shape of the nose. The motivation for rhinoplasty may be to change the appearance of the nose, improve breathing or both. The upper portion of the structure of the nose is bone, and the lower portion is cartilage.
A technical explanation of the set of surgical instruments that a doctor may ask for in the performance of operations.
Cataract surgery involves replacing the cloudy lens inside your eye with a clear artificial lens, called an intraocular lens (IOL).
A dental bone graft is necessary when bone loss has occurred in the jaw. This procedure is commonly performed prior to dental implant placement or when bone loss is negatively affecting neighboring teeth.
Please take note that surgical operations take years of study to perform, and that the material on these links may be graphic and unsettling to some people. Do not click unless you wish to see videos of actual surgery.
Attending college offers benefits beyond academic learning. Students are exposed to diverse perspectives that challenge their thinking. This fosters problem-solving and communication. College is also about social skills. Whether through student organizations or sports teams, students develop leadership skills and build lasting friendships.
This website is not affiliated with any educational institution, and all trademarks are the exclusive property of the respective owners. All copyrighted works on this website are offered for educational purposes only, governed by the four-factor rule, section 107 of the Copyright Act. CampusInspector.com is the work of a group of students in Bangkok, using data from the US Department of Education, Postsecondary Education Data System (IPEDS). If any information is incorrect, please contact us with updates.